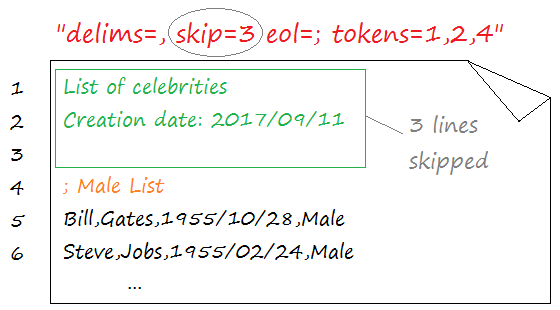
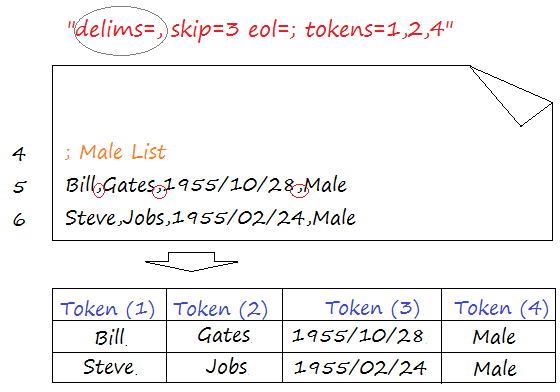
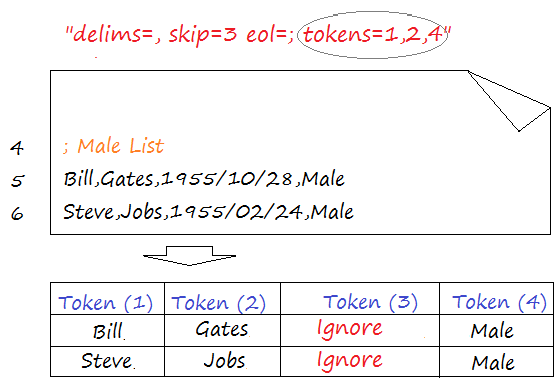
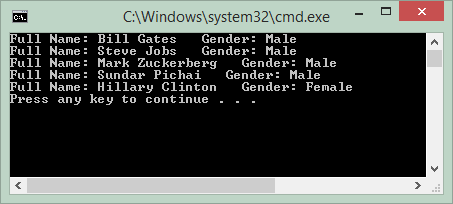
Host is not allowed to connect to this MySQL server
- Enable remote connections from the config
- Create a new user and allow it to connect to the database server from the specific host (or all hosts)
- Flush privileges
Enable Remote connections from MySQL config
/etc/mysql/my.cnf or /etc/my.cnf or /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf. The location of the MySQL configuration file depends on the version of MySQL you’re using. Check all of these locations to see if you can find the configuration file. Please join our Discord server and let us know if you haven’t found the config file yet. Perhaps we can assist you.
Once found the config file, open it and comment out the line bind-address = 127.0.0.1.
Just add # before the line to comment it out.
# bind-address = 127.0.0.1
Create new MySQL user
Login to MySQL as root –
sudo mysql
Or
mysql -u root -pDepending on the method you select, you will be prompted to enter your password. sudo password if you’re logging in with sudo.
Once in the MySQL command-line, create a new user –
> CREATE USER 'username'@'ip-address' IDENTIFIED BY 'set-password';You should see the following message if the new user is created –
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON database_name.* TO 'username'@'ip-address';Once done, please flush the privileges for the changes to take effect.
> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;Allow all remote connections
As in the preceding command, I instructed to replace the ip-address with the remote computer’s IP address. Only connections from that remote computer will be permitted. However, we can also use the ‘%’ wildcard to allow all connections, regardless of whether they are from your computer or from that basement guy who needs access to your database for personal reasons. 😉 They will, however, need to enter the correct credentials to access the database.
> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON database_name.* TO 'username'@'%';Allow connections from a range of IP address
If the remote servers are on the same network, their IP addresses can easily be allowed to allow remote connections without the need for multiple MySQL users.
> GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON database_name.* TO 'username'@'172.19.0.*';Notice how the last octet of the IP address has been replaced with * in the above command. This allows all servers with that IP address to begin with 172.19.0.